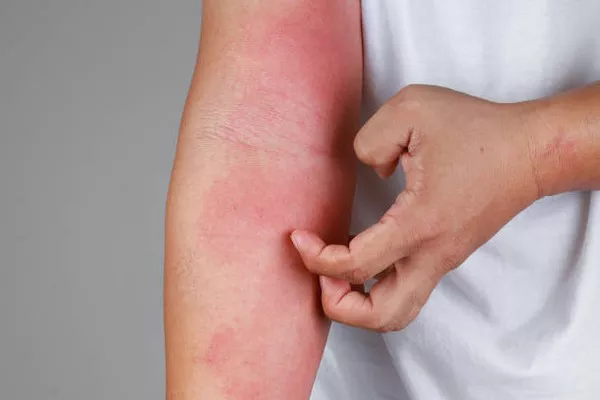
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a common skin condition characterized by raised, itchy welts on the skin. It can be a temporary inconvenience or a chronic issue for some individuals. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of hives, including its duration, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. By breaking down complex medical information into simple sentences, we hope to make the information accessible and understandable for all readers.
What are Hives?
Hives are a type of skin reaction that appears as red, raised, itchy bumps or welts on the skin. They can vary in size and shape and can appear anywhere on the body. Hives are caused by the release of histamine, a chemical in the body that causes blood vessels to expand and allows fluid to leak into the skin.
Duration of Hives
The duration of hives can vary greatly from person to person. For most people, hives last for a few hours to a few days. This is known as acute urticaria. However, in some cases, hives can persist for more than six weeks, which is considered chronic urticaria.
Causes of Hives
There are many potential causes of hives, including:
Allergies: Common allergens include foods, medications, and insect bites.
Physical triggers: These can include heat, cold, sunlight, and pressure.
Infections: Some viral or bacterial infections can cause hives.
Autoimmune diseases: In some cases, the body’s immune system may mistakenly attack its own tissues, leading to hives.
Stress: Emotional stress can sometimes trigger hives.
Hormonal changes: Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation or pregnancy can also cause hives.
Symptoms of Hives
The primary symptom of hives is the appearance of itchy, red welts on the skin. These welts can be small or large and may change in size and shape over time. Other symptoms may include:
- Swelling of the face, lips, or tongue
- Difficulty breathing
- Throat tightness
- Abdominal pain
- Diagnosis of Hives
Diagnosing hives typically involves a physical examination and a discussion of the patient’s medical history. The doctor will ask about the duration and pattern of the hives, any potential triggers, and any accompanying symptoms. In some cases, additional tests may be needed to rule out other conditions or identify specific triggers.
Treatment of Hives
Treatment for hives is aimed at relieving symptoms and identifying and avoiding triggers. Some common treatments include:
Antihistamines: These medications can help reduce itching and swelling.
Corticosteroids: For more severe cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation.
Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding triggers can help prevent future outbreaks.
Cold compresses: Applying a cold compress to the affected area can help relieve itching and swelling.
Management of Chronic Hives
For those with chronic hives, long-term management may be necessary. This can include:
Regular use of antihistamines
Immunomodulatory therapy: In some cases, medications that affect the immune system may be used.
Lifestyle changes: Reducing stress and avoiding known triggers can help manage chronic hives.
Prevention of Hives
While it may not always be possible to prevent hives, especially in cases where the cause is unknown, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of outbreaks:
Identify and avoid allergens: If you know what causes your hives, avoiding these triggers can help prevent future episodes.
Use non-irritating skincare products: Choose gentle, fragrance-free products to reduce the chance of skin irritation.
Wear loose clothing: Tight clothing can sometimes irritate the skin and trigger hives, so opt for loose, breathable fabrics.
Manage stress: Since stress can be a trigger for some people, incorporating stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or regular exercise can be beneficial.
Stay cool: If heat is a trigger, try to stay in cooler environments and avoid hot baths or showers.
The Impact of Hives on Daily Life
Hives can significantly impact a person’s daily life, especially if they are severe or persistent. The itching and discomfort can interfere with work, social activities, and sleep. Chronic hives can also take a toll on mental health, leading to anxiety and depression. It’s important for individuals with hives to seek support from friends, family, and healthcare providers to manage these challenges.
Conclusion
Hives can be a frustrating and uncomfortable condition, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals manage and cope with this skin condition. Whether hives are acute or chronic, seeking medical advice and following a treatment plan can lead to relief and improved quality of life.
Related Topics: