Feather allergy is an allergic condition that occurs when the immune system overreacts to proteins present in feathers. Feathers are commonly found in pillows, bedding, upholstered furniture, and clothing items such as down jackets. This allergy can cause a range of uncomfortable and sometimes severe symptoms, which can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. Understanding the symptoms of feather allergy is crucial for proper diagnosis and management.
Skin Symptoms
Hives: Hives are itchy, raised welts on the skin that can appear shortly after exposure to feathers. They can vary in size and shape and may occur anywhere on the body. For example, a person who sleeps on a feather pillow might wake up with hives on their face, neck, or arms. The hives are caused by the release of histamine and other chemicals in the skin as part of the allergic reaction. They can be extremely itchy and may cause discomfort and a burning sensation.
Eczema Exacerbation: For individuals who already have eczema, exposure to feathers can exacerbate the condition. Eczema is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Feather allergens can trigger a flare-up, leading to increased redness, swelling, and itching. The skin may become scaly and cracked, especially in areas that have come into contact with feathers. For instance, a person with eczema on their hands might notice a worsening of the condition after handling a feather-filled cushion.
Contact Dermatitis: Direct contact with feathers can cause contact dermatitis, which is a type of skin inflammation. The skin at the contact site may become red, swollen, and itchy. It can also develop a rash or small blisters. This is more likely to occur if the feathers are in direct and prolonged contact with the skin, such as when wearing a feather-trimmed garment or using a feather comforter. For example, a person who wears a feather boa around their neck for an extended period might develop contact dermatitis on their neck area.
Respiratory Symptoms
Sneezing: Sneezing is a common respiratory symptom of feather allergy. It can occur in bouts and may be accompanied by a runny or stuffy nose. The sneezing is triggered by the inhalation of feather allergens, which irritate the nasal passages. A person might start sneezing uncontrollably when entering a room with a feather-filled duvet or pillow. This can be very bothersome and disrupt daily activities.
Nasal Congestion: Feather allergens can cause the nasal passages to become inflamed and congested. This makes it difficult to breathe through the nose and can lead to a feeling of fullness in the sinuses. The congestion may be mild or severe, and in some cases, it can cause a headache due to the pressure build-up. For example, a person with a feather allergy might have a constantly stuffy nose when sleeping on a feather mattress.
Wheezing: Wheezing is a whistling sound that occurs when breathing, especially during expiration. It is caused by the constriction of the airways due to the allergic reaction. Feather allergy can cause the muscles around the airways to tighten and the airways to become inflamed and narrowed. This can make breathing difficult and may lead to shortness of breath. A person with a feather allergy might experience wheezing when cleaning a room with feather dusters or when in close proximity to a large number of feathers.
Coughing: Coughing is another respiratory symptom that can be triggered by feather allergy. It may be a dry cough or a cough with phlegm. The cough is the body’s attempt to clear the airways of the allergens and the mucus that is produced as a result of the allergic reaction. A person might have a persistent cough, especially at night when lying on a feather pillow.
Eye Symptoms
Itchy Eyes: Itchy eyes are a very common symptom of feather allergy. The eyes may feel extremely itchy and may cause a person to rub them frequently. This rubbing can further irritate the eyes and may lead to redness and swelling. The itchiness is caused by the allergic reaction in the conjunctiva, the thin membrane that covers the front of the eye. For example, a person who sits on a feather-stuffed couch and then rubs their eyes may experience intense itching.
Red and Watery Eyes: The eyes may become red and watery due to the allergic reaction. The blood vessels in the conjunctiva dilate, giving the eyes a red appearance. Tears are produced in an attempt to flush out the allergens. This can make vision blurry and cause discomfort. A person with a feather allergy might have constantly red and watery eyes when in a room with feather decorations.
Swelling of the Eyelids: In some cases, the eyelids can swell as a result of the allergic reaction. This can make it difficult to open the eyes fully and may affect a person’s appearance. The swelling is caused by the accumulation of fluid in the tissues around the eyes. For example, a person who sleeps with a feather pillow might wake up with swollen eyelids.
Generalized Symptoms
Fatigue: Dealing with the constant symptoms of a feather allergy can lead to fatigue. The body is constantly in a state of trying to fight off the allergic reaction, which can be exhausting. A person might feel tired even after a full night’s sleep if they are sleeping on feather bedding. This fatigue can affect their ability to concentrate and perform daily tasks effectively.
Headache: Headaches can occur as a result of the combination of nasal congestion, sinus pressure, and the overall stress on the body due to the allergic reaction. The pain can range from a mild ache to a severe throbbing headache. For example, a person with a feather allergy might experience a headache after spending a few hours in a room with a lot of feather products.
Anaphylactic Shock (Rare but Severe)
Sudden Onset of Symptoms: Although rare, anaphylactic shock can occur in severe cases of feather allergy. It usually has a sudden onset and involves multiple body systems. A person might suddenly experience difficulty breathing, a rapid drop in blood pressure, and a feeling of lightheadedness. For example, a person who accidentally inhales a large amount of feather dust might immediately go into anaphylactic shock.
Life-Threatening Consequences: Anaphylactic shock is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. If not treated promptly with epinephrine and other emergency measures, it can lead to loss of consciousness, cardiac arrest, and death. A person with a known severe feather allergy should always carry an epinephrine auto-injector and know how to use it in case of an emergency.
Diagnosis and Management
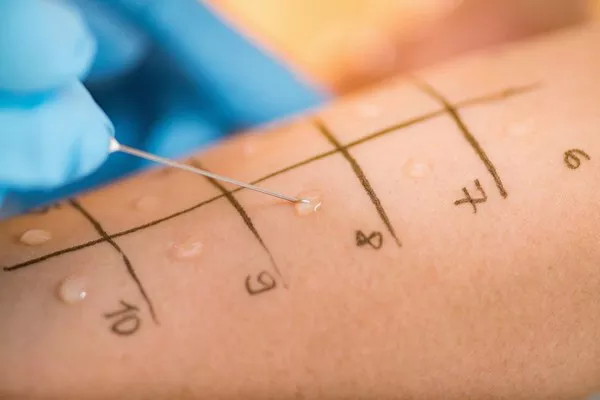
Diagnostic Tests: To diagnose a feather allergy, a doctor may perform skin prick tests or blood tests. In a skin prick test, a small amount of a liquid containing feather proteins is placed on the skin and then pricked. If a person is allergic, a raised, red bump will appear. Blood tests measure the levels of specific IgE antibodies to feather proteins. However, a positive test result does not always mean a person will have clinical symptoms.
Management Strategies: The best way to manage a feather allergy is to avoid exposure to feathers. This means replacing feather pillows, bedding, and upholstered furniture with non-feather alternatives. Using allergen-proof covers on mattresses and pillows can also help. In case of symptoms, over-the-counter antihistamines can relieve itching, sneezing, and other mild symptoms. Nasal corticosteroid sprays can help with nasal congestion. For severe symptoms or anaphylactic shock, immediate medical attention and the use of epinephrine are essential.
Conclusion
Feather allergy can present with a variety of symptoms affecting the skin, respiratory system, eyes, and overall well-being. Recognizing these symptoms is important for early diagnosis and appropriate management. By avoiding feather exposure and using proper medical treatments when needed, individuals with feather allergy can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of this allergic condition. It is also crucial for healthcare providers to be aware of the symptoms and diagnostic methods to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plans.
Related topics
- What Test Is Done for Allergy?
- What Does Histamine Do in an Allergic Reaction?
- What Is the Most Serious Type of Latex Allergy?