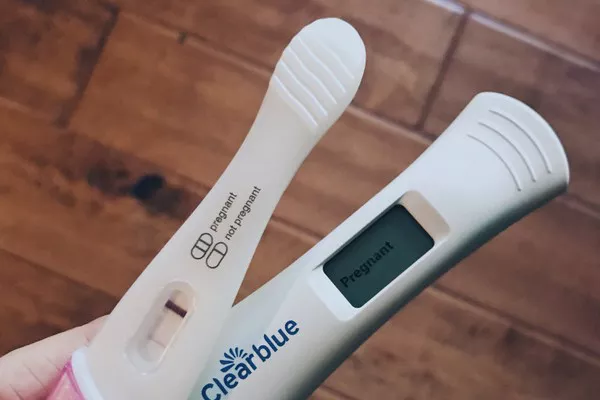
Home pregnancy tests have revolutionized the way individuals confirm their pregnancy status, providing convenient and accessible means for early detection. These tests detect the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced by the placenta shortly after conception. Understanding how to use home pregnancy tests effectively and interpret their results accurately is crucial for individuals seeking to confirm pregnancy in the comfort of their homes. In this article, we explore the principles behind home pregnancy tests, step-by-step instructions for their use, factors affecting test accuracy, and when to consult a healthcare provider.
Overview of hCG and Pregnancy Testing:
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone produced by the placenta following implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterine lining. hCG plays a pivotal role in maintaining the corpus luteum, a temporary endocrine structure that secretes progesterone to support early pregnancy. The levels of hCG rise rapidly in the early stages of pregnancy, doubling approximately every 48-72 hours during the first trimester.
Home pregnancy tests (HPTs) utilize immunochromatographic assays to detect hCG in urine samples. These tests typically consist of a strip or cassette containing antibodies that bind specifically to hCG molecules. When a urine sample containing hCG is applied to the test strip, the hCG molecules bind to the antibodies, causing a visible color change that indicates a positive result.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Home Pregnancy Tests:
1. Selecting a Home Pregnancy Test: Choose a reputable brand of home pregnancy test from a pharmacy or retail store. Look for tests that offer high sensitivity and accuracy in detecting low levels of hCG. Consider factors such as cost, ease of use, and digital versus non-digital display options.
2. Timing of Testing: Home pregnancy tests are most reliable when performed after a missed period, although some tests claim to detect hCG several days before the expected period. Follow the instructions provided with the test kit regarding the recommended timing for testing relative to the expected menstrual cycle.
3. Collecting Urine Sample: Use a clean, dry container to collect a urine sample for testing. Some home pregnancy tests offer the option of holding the test strip directly in the urine stream during urination, while others require dipping the test strip into a cup containing the urine sample. Follow the specific instructions provided with the test kit.
4. Performing the Test: Remove the test strip from its packaging and hold it by the handle or grip area to avoid contact with the absorbent portion of the strip. If using a urine stream test, hold the absorbent tip in the urine stream for the specified duration (usually a few seconds). If dipping the test strip into a urine sample, immerse the absorbent tip into the urine for the specified time period (usually a few seconds).
5. Waiting for Results: After performing the test, lay the test strip flat on a clean, dry surface and wait for the specified amount of time (usually 3-5 minutes) for the results to develop. Avoid disturbing the test strip during this time to prevent inaccurate results.
6. Interpreting Results: Check the test strip for the presence of visible lines or symbols indicating a positive or negative result. Most home pregnancy tests display results using lines, symbols, or digital readouts. A single line or symbol typically indicates a negative result, while two lines or symbols indicate a positive result. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for interpreting results, as some tests may have variations in result display.
7. Recording Results: Record the results of the home pregnancy test, including the date of testing and any relevant observations, in a journal or pregnancy diary. Documenting test results can help track changes over time and provide valuable information for healthcare providers.
Factors Affecting Home Pregnancy Test Accuracy:
While home pregnancy tests are generally accurate when used correctly, several factors can affect their reliability and accuracy:
Timing of Testing: Testing too early in the menstrual cycle, before hCG levels have risen sufficiently to be detected by the test, can result in false-negative results. It is recommended to wait until after a missed period for optimal accuracy.
Quality of Test Kit: The sensitivity and accuracy of home pregnancy tests can vary depending on the brand and quality of the test kit. Choose a reputable brand with a track record of reliability and accuracy.
User Error: Incorrectly performing the test, misinterpreting results, or using expired test kits can lead to inaccurate results. Follow the instructions provided with the test kit carefully and ensure proper storage and handling of the test.
Medications and Medical Conditions: Certain medications and medical conditions, such as fertility treatments, hormonal therapies, and ectopic pregnancy, can interfere with hCG levels and affect the accuracy of home pregnancy tests. Consult a healthcare provider if you have concerns about the potential impact of medications or medical conditions on test results.
Chemical Pregnancy: In some cases, a positive home pregnancy test may indicate a chemical pregnancy, where a fertilized egg implants in the uterus briefly before being naturally expelled. Chemical pregnancies are characterized by early miscarriage and may result in a positive test followed by a negative test or delayed menstrual period.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider:
While home pregnancy tests are convenient and reliable for confirming pregnancy, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for confirmation and further evaluation, especially in the following situations:
Uncertain Results: If you are unsure about the results of a home pregnancy test or if the results are inconclusive, consult a healthcare provider for confirmation and guidance.
Persistent Symptoms: If you experience persistent symptoms of pregnancy, such as nausea, fatigue, breast tenderness, or missed periods, but repeatedly receive negative home pregnancy test results, seek medical evaluation to rule out other potential causes.
History of Pregnancy Complications: Individuals with a history of pregnancy complications, such as miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or infertility, may require specialized monitoring and evaluation by a healthcare provider to ensure optimal maternal-fetal health.
Concerns about Test Accuracy: If you have concerns about the accuracy or reliability of home pregnancy tests, or if you suspect underlying medical conditions or medications may affect test results, consult a healthcare provider for further assessment and guidance.
See Also: Genetic Testing During Pregnancy: Purposes, Types & Process
Conclusion:
Home pregnancy tests offer individuals a convenient and accessible means of confirming pregnancy status in the comfort of their homes. By understanding the principles behind home pregnancy tests, following step-by-step instructions for their use, and being aware of factors affecting test accuracy, individuals can obtain reliable results and make informed decisions about their reproductive health. While home pregnancy tests are generally accurate when used correctly, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider for confirmation and further evaluation, especially in cases of uncertain results or persistent symptoms. Continued advancements in pregnancy testing technologies and healthcare delivery models hold promise for improving access to timely and accurate pregnancy diagnosis worldwide.