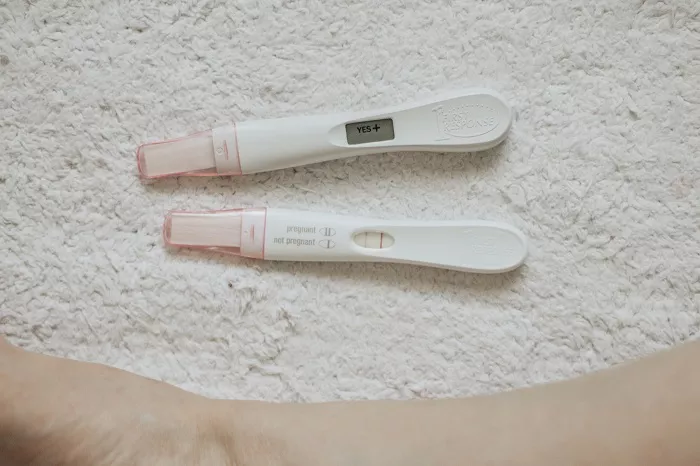
The confirmation of pregnancy is a crucial and often eagerly anticipated event. Understanding the timeline within which pregnancy can be accurately detected is essential for women who suspect they might be expecting. It not only provides peace of mind but also enables early initiation of prenatal care, which is vital for the health of both the mother and the developing fetus.
Implantation and the Onset of Hormonal Changes
Implantation is a significant milestone in the early stages of pregnancy. It typically occurs around 6 to 12 days after fertilization. Once the fertilized egg implants into the uterine lining, the body initiates a series of hormonal changes. The most notable of these is the production of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This hormone is the key target of pregnancy tests. For example, if a woman ovulates on day 14 of her menstrual cycle and fertilization occurs promptly, implantation might take place around day 20 – 22. However, the exact timing of implantation can vary among individuals. Some women may experience implantation bleeding or spotting, which can serve as an early indication that implantation has happened, although not all women have this symptom. The rise in hCG levels after implantation is gradual at first and then accelerates.
Early Detection with Sensitive Pregnancy Tests
Early pregnancy tests have become increasingly popular as they claim to detect pregnancy even before a missed period. These tests are designed to identify very low levels of hCG. They can potentially provide a positive result as early as 7 to 10 days after ovulation. Nevertheless, the accuracy of these early tests is not as high as when testing after a missed period. The hCG levels in the initial days following implantation are relatively low, and there is a greater likelihood of obtaining a false negative result. For instance, a woman who tests too early might receive a negative result despite being pregnant because the hCG concentration has not reached the detectable threshold of the test. Different early pregnancy test kits have varying sensitivities, with some being able to detect hCG levels as low as 10 mIU/mL, while others may require a higher concentration. It is crucial for women to carefully read and understand the instructions of the test kit they are using.
Testing After a Missed Menstrual Period
Testing after a missed period is generally regarded as the most reliable time to confirm pregnancy. In a regular 28 – day menstrual cycle, a missed period usually indicates that it has been around 14 days since ovulation. By this time, the hCG levels have had sufficient time to increase. Most over – the – counter pregnancy tests are highly accurate when used at this stage. A missed period is a strong indication of a possible pregnancy, and a pregnancy test can provide a definite answer. However, if a woman has an irregular menstrual cycle, the timing of the missed period and the optimal testing time will be different. For example, if a woman has a 35 – day cycle, her missed period might occur around day 35, and testing a few days after that would be more appropriate.
Blood Tests for Precise Detection
Blood tests offer another avenue for confirming pregnancy and can detect it even earlier than some urine tests. There are two main types of blood tests. A qualitative blood test simply determines the presence or absence of hCG and gives a binary result, similar to a urine test. It can detect pregnancy as early as 10 to 12 days after ovulation. On the other hand, a quantitative blood test measures the exact amount of hCG in the blood. This is particularly useful in monitoring the progress of a pregnancy, especially in cases where there is a concern about miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. The quantitative blood test can detect extremely low levels of hCG and is more accurate than many urine tests. However, it requires a visit to a healthcare facility and is more expensive and time – consuming compared to a home urine test.
Ultrasound: Visual Confirmation of Pregnancy
Ultrasound is a valuable tool in confirming pregnancy and provides additional information about the pregnancy. Transvaginal ultrasounds can detect a gestational sac as early as 4 to 5 weeks after the last menstrual period. This corresponds to approximately 2 to 3 weeks after ovulation. At this early stage, the ultrasound may only show a small sac and not a clearly visible embryo. Abdominal ultrasounds, which are less invasive but also less sensitive in the early stages, can usually detect pregnancy around 6 weeks after the last menstrual period. Ultrasound is not only used for confirming pregnancy but also for determining the location of the pregnancy (whether it is intrauterine or ectopic) and estimating the gestational age. It is a more comprehensive but also more costly and technically demanding method compared to simple urine or blood tests.
Factors Influencing the Confirmation Timeline
Several factors can affect the timeline within which pregnancy is confirmed. The regularity of a woman’s menstrual cycle is a significant factor. Women with irregular cycles may have difficulty predicting ovulation accurately, which in turn affects the optimal testing time. The sensitivity of the test being used, whether it is a urine test, qualitative blood test, or quantitative blood test, also plays a crucial role. Additionally, certain medical conditions and medications can interfere with hCG levels and the accuracy of the tests. For example, some fertility drugs can increase hCG levels, leading to a false positive result. Women with conditions like ovarian cysts or certain types of cancer may also have elevated hCG levels, which can complicate the interpretation of test results. It is essential for women to inform their healthcare providers about any medications they are taking or pre – existing medical conditions before attempting to confirm pregnancy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the confirmation of pregnancy occurs within a range of time frames and depends on multiple factors. Implantation and the subsequent rise in hCG levels set the stage for detection. Early pregnancy tests can potentially detect pregnancy relatively early, but with some limitations in accuracy. Testing after a missed period is more reliable. Blood tests offer greater precision and the ability to monitor hCG levels. Ultrasound provides visual confirmation and additional details about the pregnancy. However, factors such as menstrual cycle regularity, test sensitivity, and underlying medical conditions must be taken into account. By understanding these aspects, women can make more informed decisions about when and how to confirm pregnancy and ensure the best possible start to their pregnancy journey with appropriate prenatal care and medical attention.
Related topics