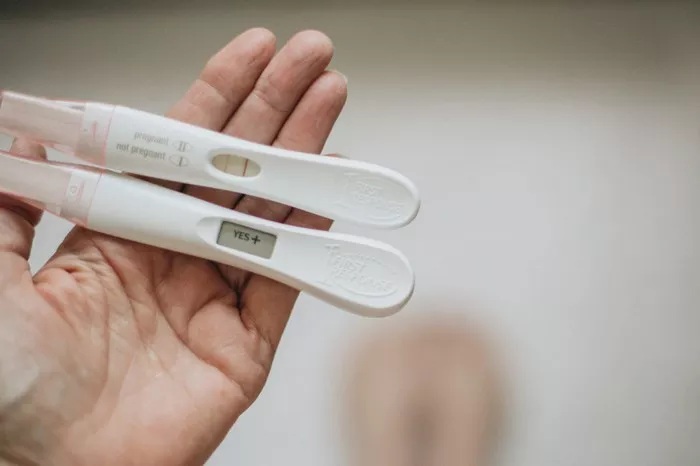
Birth control methods are highly effective at preventing pregnancy, but no method is 100% foolproof. Women using contraception may still wonder whether they can experience signs of pregnancy while on birth control. Understanding how birth control works, the potential signs of pregnancy, and the factors that can lead to an unplanned pregnancy can help clarify this concern.
How Does Birth Control Work?
Different forms of birth control work in various ways to prevent pregnancy. The effectiveness of each method depends on proper use and adherence.
1. Hormonal Birth Control
Hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, patches, injections, and hormonal intrauterine devices (IUDs), work by:
- Preventing ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovaries).
- Thickening cervical mucus to block sperm from reaching the egg.
- Thinning the uterine lining, making it less receptive to a fertilized egg.
2. Barrier Methods
Barrier methods, including condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps, physically prevent sperm from entering the uterus.
3. Intrauterine Devices (IUDs)
There are two types of IUDs: hormonal and copper. Hormonal IUDs release progestin to prevent ovulation and thicken cervical mucus, while copper IUDs create an environment that is toxic to sperm.
4. Permanent Methods
Tubal ligation (for women) and vasectomy (for men) are permanent contraceptive methods that block the reproductive pathways.
5. Emergency Contraception
Emergency contraceptive pills (morning-after pills) are used after unprotected sex to prevent pregnancy by delaying ovulation or preventing implantation.
Can You Get Pregnant While on Birth Control?
Although birth control is highly effective when used correctly, certain factors can reduce its effectiveness and increase the risk of pregnancy.
1. Missed or Incorrect Use of Birth Control
- Forgetting to take birth control pills consistently can increase the risk of ovulation.
- Not replacing patches, rings, or injections on time can reduce hormone levels.
- Improper use of condoms or diaphragms (e.g., not using spermicide) can increase the chance of pregnancy.
2. Medication Interference
Certain medications can reduce the effectiveness of hormonal birth control, including:
- Antibiotics such as rifampin
- Antiepileptic drugs
- Antifungal medications
- St. John’s Wort (a herbal supplement)
3. Gastrointestinal Issues
Vomiting or severe diarrhea shortly after taking an oral contraceptive can prevent proper absorption, making it less effective.
4. Expulsion of an IUD
In rare cases, an intrauterine device (IUD) may become dislodged or expelled, increasing the risk of pregnancy.
Signs of Pregnancy While on Birth Control
Women who suspect pregnancy while using birth control should watch for early pregnancy symptoms. These signs may be similar to hormonal fluctuations caused by contraceptive use, making them difficult to distinguish.
1. Missed Period
One of the earliest signs of pregnancy is a missed period. However, some hormonal birth control methods, such as progestin-only pills, implants, or hormonal IUDs, can cause lighter periods or even stop menstruation, making this sign less reliable.
2. Breast Tenderness
Pregnancy can cause increased breast sensitivity, swelling, and tenderness. This symptom can also be a side effect of hormonal birth control, so it may not always indicate pregnancy.
3. Nausea and Morning Sickness
Nausea, particularly in the morning, is a common pregnancy symptom. Some women on birth control may experience nausea as a side effect, but persistent morning sickness could indicate pregnancy.
4. Fatigue
Extreme tiredness and low energy levels are common in early pregnancy due to hormonal changes. While birth control can also cause fatigue, sudden and excessive tiredness may suggest pregnancy.
5. Frequent Urination
Pregnant women may notice an increased need to urinate due to hormonal shifts and increased blood flow to the kidneys. If this symptom appears unexpectedly, pregnancy might be a possibility.
6. Changes in Appetite or Food Aversions
Pregnancy hormones can alter taste preferences, causing cravings or aversions to certain foods. While birth control can cause mild appetite changes, drastic shifts in food preferences may suggest pregnancy.
7. Light Spotting or Implantation Bleeding
Some women experience light spotting around the time of implantation, which can be mistaken for a light period. Spotting can also occur due to hormonal changes from birth control.
8. Mood Swings
Fluctuating hormone levels in pregnancy can lead to emotional changes, such as increased irritability, sadness, or anxiety. Birth control can also cause mood swings, but sudden, intense emotional changes might signal pregnancy.
What to Do If You Suspect Pregnancy on Birth Control
If you are experiencing symptoms that suggest pregnancy while using birth control, it is important to take the following steps:
1. Take a Home Pregnancy Test
Home pregnancy tests detect the presence of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone produced during pregnancy. These tests are most accurate when taken after a missed period.
2. Consult a Healthcare Provider
If the pregnancy test is positive or if symptoms persist despite a negative test, consult a doctor for further evaluation. A blood test or ultrasound may be needed to confirm pregnancy.
3. Continue or Discontinue Birth Control Based on Medical Advice
If pregnancy is confirmed, discuss with a healthcare provider whether to discontinue birth control. Some hormonal contraceptives should be stopped immediately, while others may require a transition plan.
4. Consider Emergency Contraception (If Necessary)
If unprotected intercourse occurs and pregnancy is not desired, emergency contraception can be used within a specific timeframe to reduce the risk of pregnancy.
Is Birth Control Harmful During Early Pregnancy?
Many women worry about the effects of birth control on an unplanned pregnancy. Fortunately, research suggests that:
- Most hormonal contraceptives do not cause birth defects or harm the developing fetus.
- However, certain contraceptives, such as progestin-only pills and hormonal IUDs, should be discontinued once pregnancy is confirmed.
Conclusion
While birth control is highly effective, pregnancy can still occur due to missed doses, medication interactions, or other factors. Women using birth control should be aware of potential pregnancy symptoms, including missed periods, nausea, fatigue, and breast tenderness. If pregnancy is suspected, taking a home pregnancy test and consulting a healthcare provider is crucial. Understanding how birth control works and recognizing signs of pregnancy can help women make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
You Might Be Interested In: