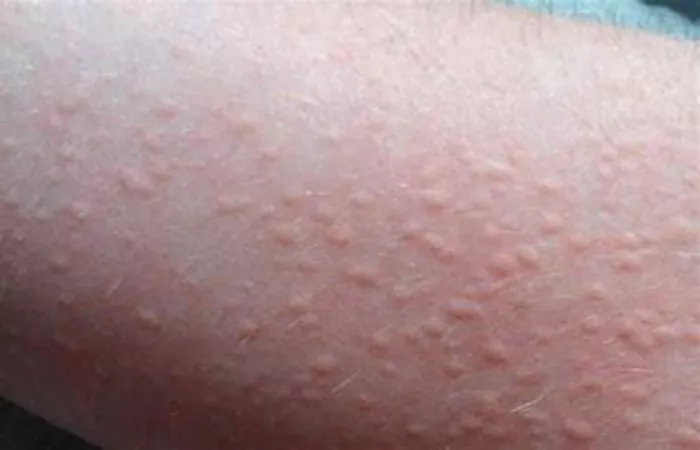
Hives, also known as urticaria, are red, itchy welts that appear on the skin due to an allergic reaction or other triggers. They can be acute (lasting less than six weeks) or chronic (lasting more than six weeks). Effective management of hives often involves using antihistamines, which work by blocking histamine, a chemical released by the immune system that causes itching and redness. This article will explore the best antihistamines for hives, their mechanisms of action, safety profiles, and suitability for long-term use.
Understanding Hives and Antihistamines
Hives occur when the immune system overreacts to allergens or other triggers, releasing histamine. This leads to symptoms like redness, swelling, and itching. Antihistamines are the first line of defense against hives, providing relief by blocking histamine receptors. They are classified into two generations:
First-Generation Antihistamines:These can cause significant drowsiness and are generally used for short-term relief.
Second-Generation Antihistamines:These are less likely to cause drowsiness and are suitable for long-term use.
9 Best Antihistamines for Hives
Second-Generation Antihistamines
These antihistamines are generally preferred for managing hives due to their non-drowsy nature and long-term safety.
Cetirizine (Zyrtec)
Form:Tablet, liquid
Effectiveness:Effective in managing hives and other allergic symptoms.
Safety:Generally non-drowsy and safe for long-term use.
Best For:People with moderate to severe hives who need long-term relief.
Loratadine (Claritin)
Form:Tablet, chewable tablet
Effectiveness:Effective in managing hives and other allergic symptoms.
Safety:Generally non-drowsy and safe for long-term use.
Best For:People with hives who need long-term relief.
Fexofenadine (Allegra)
Form:Tablet, liquid
Effectiveness:Effective in managing hives and other allergic symptoms.
Safety:Generally non-drowsy and safe for long-term use.
Best For:People with hives who need long-term relief.
Levocetirizine (Xyzal)
Form:Tablet
Effectiveness:Highly effective in managing hives and other allergic symptoms.
Safety:Generally non-drowsy and safe for long-term use.
Best For:People with moderate to severe hives who need long-term relief.
First-Generation Antihistamines
These antihistamines are effective but can cause significant drowsiness. They are generally used for short-term relief.
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
Form:Tablet, liquid gel capsules
Effectiveness:Effective in managing hives and other allergic symptoms.
Safety:May cause drowsiness and is not suitable for long-term use.
Best For:People needing quick relief from severe hives, especially at night.
Hydroxyzine (Atarax)
Form:Tablet, liquid
Effectiveness:Effective in managing hives and other allergic symptoms.
Safety:May cause drowsiness and is not suitable for long-term use.
Best For:People needing quick relief from severe hives, especially at night.
Prescription Antihistamines
These antihistamines are available by prescription and are used for more severe cases.
Desloratadine (Clarinex)
Form:Tablet
Effectiveness:Effective in managing hives and other allergic symptoms.
Safety:Generally non-drowsy and safe for long-term use.
Best For:People with severe hives who need long-term relief.
H2 Blockers
H2 blockers are sometimes used in combination with antihistamines to provide additional relief.
Famotidine (Pepcid)
Form:Tablet
Effectiveness:Effective in reducing redness and swelling when used in combination with antihistamines.
Safety:Generally safe with minimal side effects.
Best For:People needing additional relief from hives.
Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists
These medications block leukotrienes, chemicals involved in allergic reactions.
Montelukast (Singulair)
Form:Tablet
Effectiveness:Effective in managing chronic hives when used in combination with antihistamines.
Safety:Generally safe but may cause side effects like headache and nausea.
Best For:People with chronic hives not responding to antihistamines alone.
Conclusion
Managing hives effectively requires the right choice of antihistamine based on your specific symptoms and needs. Second-generation antihistamines like cetirizine, loratadine, fexofenadine, and levocetirizine provide effective relief from hives and other allergic symptoms. First-generation antihistamines like diphenhydramine and hydroxyzine offer quick relief but should be used short-term. Prescription antihistamines like desloratadine can be beneficial for severe cases. H2 blockers like famotidine can provide additional relief when used in combination with antihistamines. Always consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for your specific needs. With the right approach, you can manage your hives and improve your overall comfort.
Relative topics:
Itchy Eye Causes: 8 Reasons Your Eyes Itch
Baby Dry Scalp: Causes, Home Remedies & When to Seek Help
7 Best Air Purifiers for Allergies and Asthma